The Physiological and Psychological Benefits of Exercise
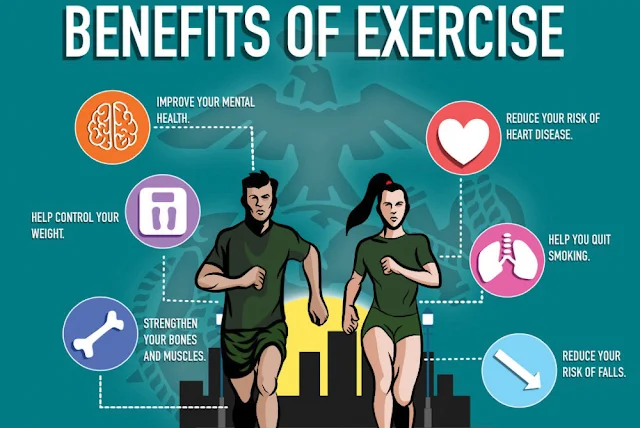
Exercise is widely recognized as a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle. Beyond its obvious physical benefits, exercise profoundly impacts psychological well-being. Understanding these multifaceted benefits can motivate individuals to incorporate regular physical activity into their daily routines. This article explores the physiological and psychological benefits of exercise, illustrating why it is essential for overall health.
Physiological Benefits of Exercise
Improved Cardiovascular Health
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, enhances blood circulation, and helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels. Aerobic exercises, such as running, cycling, and swimming, are particularly effective in reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Studies have shown that consistent exercise can lower bad cholesterol (LDL) and increase good cholesterol (HDL), contributing to a healthier heart.
Enhanced Muscular Strength and Endurance
Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting and resistance training, are vital for building and maintaining muscle mass. These activities improve muscular strength, endurance, and overall physical performance. Increased muscle mass boosts metabolism, aiding in weight management and reducing the risk of obesity.
Better Bone Health
Weight-bearing exercises, like walking, running, and resistance training, play a crucial role in maintaining bone density. These activities stimulate bone formation and slow down bone loss, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, especially in older adults.
Boosted Immune System
Regular moderate exercise can enhance the immune system by promoting good circulation, which allows immune cells to move efficiently throughout the body. This increased circulation helps the body fight off illnesses more effectively and can lead to fewer colds and infections.
Improved Metabolic Function
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood sugar levels, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or at risk of developing the condition. Regular physical activity aids in maintaining a healthy weight, further enhancing metabolic health.
Enhanced Respiratory Function
Aerobic exercises increase lung capacity and improve the efficiency of the respiratory system. This leads to better oxygen uptake and utilization, enhancing overall endurance and reducing the sensation of breathlessness during physical activities.
Psychological Benefits of Exercise
Reduced Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing mental health conditions like depression and anxiety. Physical activity triggers the release of endorphins, often referred to as "feel-good" hormones, which can alleviate symptoms of depression. Additionally, exercise reduces levels of cortisol, a stress hormone, thereby lowering anxiety levels.
Enhanced Mood and Emotional Well-being
Regular physical activity is associated with improved mood and emotional stability. Exercise promotes the release of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play key roles in regulating mood and promoting feelings of happiness and relaxation.
Improved Cognitive Function
Exercise has been shown to enhance cognitive abilities, including memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, promoting the growth of new neurons and improving overall brain function. This is particularly important for older adults, as regular exercise can help prevent cognitive decline and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Increased Self-esteem and Body Image
Engaging in regular physical activity can lead to improvements in body image and self-esteem. Achieving fitness goals, whether it's running a certain distance or lifting a specific weight, boosts self-confidence. The physical changes associated with regular exercise, such as weight loss and muscle toning, also contribute to a more positive self-perception.
Stress Relief
Exercise is an effective stress reliever. Physical activity helps relax the muscles and alleviate tension in the body. It also encourages the production of endorphins and other neurotransmitters that promote a sense of calm and well-being. Activities like yoga and tai chi are particularly effective for stress management, combining physical movement with mindfulness and deep breathing techniques.
Better Sleep Quality
Regular exercise can significantly improve sleep quality by helping to regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Physical activity increases the time spent in deep sleep, the most physically restorative phase of sleep. Exercise also helps alleviate insomnia and other sleep disorders by reducing anxiety and depressive symptoms that can interfere with sleep.
Conclusion
The physiological and psychological benefits of exercise underscore its importance for maintaining overall health and well-being. From improving cardiovascular health and strengthening muscles to enhancing mood and cognitive function, the positive effects of regular physical activity are extensive and well-documented. Incorporating a variety of exercises into your routine can help you reap these benefits, leading to a healthier, happier, and more fulfilling life. Whether it's through aerobic activities, strength training, or mindfulness-based exercises like yoga, finding a form of physical activity that you enjoy and can stick with is key to long-term success.


.jpeg)
.jpg)
0 Comments